If your Jeep Compass won’t crank or start despite functioning lights and electronics, it can be frustrating. Even though the battery appears to have sufficient charge for accessories, essential systems needed for ignition may not be working.
Before seeking roadside assistance or a tow truck, it’s important to troubleshoot common issues that could be causing the problem.
By carefully checking the battery connections, fuel delivery system, ignition and sensor components, and engine mechanical condition, you can identify the underlying cause of the starting issue and address it accordingly.
This guide delves into the prevalent issues that hinder the engine from starting while the dashboard electronics are still on in a Jeep Compass.
Troubleshooting the Issue: Why Your Jeep Won’t Crank
When you turn the key and the interior lights and dashboard illuminate, but the engine doesn’t crank, there are several possible reasons. The battery might have enough charge to power the electronics, but insufficient amps to engage the starter motor.
Specific electrical issues, such as faults in the starter relay or neutral safety switch circuits, can also prevent the starter from operating. Occasionally, the starter itself malfunctions even if the battery has enough voltage to operate accessories. Problems in the fuel delivery system can also lead to a no-start situation, despite the electronics functioning properly.
Without fuel, there is no combustion and the engine internals won’t rotate when you try to start the car. In addressing each potential cause, we will discuss DIY solutions as well as situations where professional diagnosis or repair is necessary. Our objective is to ensure your Jeep Compass starts reliably once again.
Causes and Solutions : Jeep Compass Won’t Start but Has Power
When a Jeep Compass is experiencing power but fails to start, there are various critical systems to examine, including the battery, fuel supply, ignition, and engine mechanical components. By systematically assessing elements within each of these areas, the underlying reason for the failure to crank can be determined.
1. Weak Battery
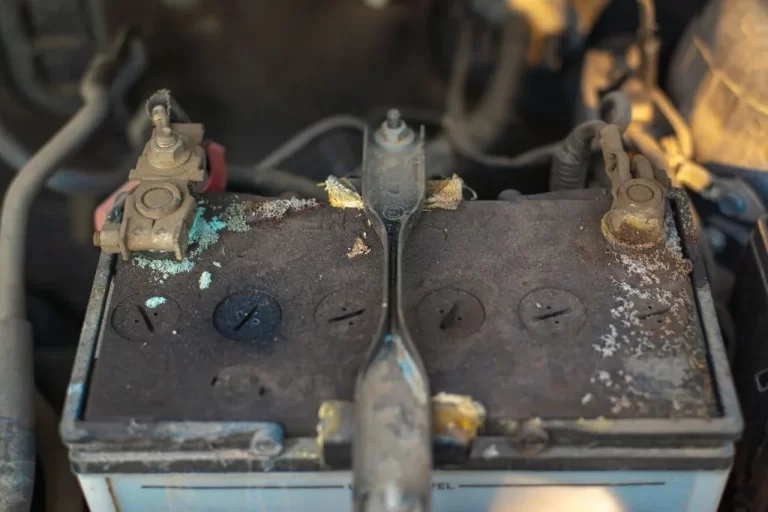
A common culprit for the inability to start even when there is power for electronics. As batteries age, they may lose capacity, resulting in enough charge to illuminate dashboard features but insufficient amperage to activate the heavy-duty starter motor.
Additional factors such as dirty terminals and loose cable connections can elevate resistance, leading to decreased current flow for ignition.
Troubleshooting
It is recommended to employ a voltmeter to gauge the battery’s charge level, with a standard reading of 12.4-12.6 volts when fully charged and maintained. Readings below 12 volts signal a potential imminent failure to start as the voltage continues to decrease.
Conducting load testing by applying a high-draw akin to the starter current can ascertain whether the battery is too feeble. Physically inspect the battery for signs of damage or leaks, which may indicate the end of its lifespan. Additionally, check the terminals and cables for corrosion and looseness, which can disrupt the complete transfer of power.
Solution
If the battery testing reveals an inability to sustain the correct voltage or pass the load test, replacing it is imperative to restore reliable starting. When installing a new battery, ensure it matches the original cold cranking amp (CCA) and capacity ratings.
Properly secure the terminals and register the new battery with the vehicle’s computer to prevent warning lights from appearing.
2. Fuel Delivery Problems

Insufficient fuel supply can hinder the starting of combustion and engine rotation, even when the batteries are strong and the electronics are functioning correctly.
Issues such as pump malfunctions, line fractures, and filter blockages can all disrupt the flow of gasoline, leading to a lack of pressurization and rendering the engine unable to start, regardless of the operational status of the electronics.
Troubleshooting
To identify fuel delivery problems, connect a fuel pressure gauge to the supply rail and have someone crank the engine to verify the presence of pressure. The absence of a pressure reading indicates a fuel delivery issue rather than ignition-related problems.
Additionally, pay attention to any lack of noise from the in-tank pump when turning the key to the start position. The absence of expected operational sounds may indicate power failures or damaged components rather than electrical malfunctions.
Solution
If diagnostics point to fuel pump or line issues, replacing the faulty parts is necessary:
- Replace failed fuel pump module/assembly
- Inspect the lines and filters for cracks or blockages caused by debris
- Utilize fuel injector cleaning additives to prevent sediment accumulation in the future
In more stubborn cases, a thorough inspection and cleaning of the tank could help dislodge sediment clusters that are obstructing the outlets. Ensuring proper fuel delivery with sufficient pressure is crucial for enabling combustion and engine rotation to facilitate successful starts.
Addressing faulty or obstructed fuel supply equipment resolves starting issues that are not related to ignition problems.
3. Ignition System Defects
If the battery voltage and fuel delivery are confirmed to be working properly, another potential cause for a vehicle’s inability to start or crank could be undisclosed problems related to the ignition system.
Malfunctions in components such as spark plugs, coil packs, wiring, and sensors can impede the generation of sparks necessary for combustion. In the absence of a visible spark, incomplete ignition of air-fuel mixtures may occur.

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting steps involve using a spark tester, which is connected to the ignition wire from the coil pack and grounded. When the engine is cranked with the help of a partner, observe for a consistent and strong spark across the tester gap.
The absence of spark suggests potential ignition issues rather than problems with the battery or fuel system. If there is a lack of spark, investigate common causes such as
- Fouled or damaged spark plugs
- Cracked plug wires
- Weak coil packs with inadequate kV output
- Corroded electrical connectors
- Faulty crankshaft and camshaft position sensors
Solution
To address the issue, replace any faulty ignition components like spark plugs, coils, and wiring, and ensure that distributor caps and rotor arm are in good condition. Additionally, verify the air gap spacing for magnetic sensors that detect the engine position. While some ignition repairs may require professional assistance, they are generally not overly complex.
4. Problems with Engine Mechanics
In rare instances where the battery, fuel system, and ignition components are functioning properly but the engine still fails to start, it could be due to underlying mechanical issues within the engine itself.
Issues such as compression problems, timing component malfunctions, internal parts being seized, or minor sensor misalignments can result in the engine not cranking or starting.

Troubleshooting
Identifying the root mechanical causes of a no-start situation requires thorough diagnostics once other systems have been ruled out. Diagnostic tests may include: Conducting a compression test by turning the crankshaft using the starter to determine if the cylinders maintain the required pressure levels. Any leaks could indicate problems with gaskets or piston rings. Checking for any slack in the timing chain or slight misalignments in the cam or crank sensor rotor positioning.
Any identified defects may necessitate disassembling the engine for repair. Identifying mechanical issues can be more challenging without the necessary tools and expertise compared to diagnosing electrical or fuel-related problems.
However, mechanical problems should not be ruled out, especially when electronic and ignition systems are functioning but the engine still fails to start.
Solution
Resolving mechanical no-start problems typically involves repairing or replacing head gaskets and piston rings that may be causing compression leaks. Ensuring proper realignment of the camshaft and crankshaft timing if they have shifted during repairs. Sometimes, the cylinders may require honing and the pistons or rings may need to be replaced to restore optimal compression.
Adjusting the spacing of the crank and cam positional sensor rotors to the manufacturer’s specifications is crucial for correct engine timing. While it is possible to attempt DIY repairs with the right skills, relying on professional mechanic services is often more practical for addressing complex mechanical issues effectively.
5. Defective Neutral Safety Switch
The neutral safety switch is a device that inhibits the engine from starting when the transmission is engaged. Malfunctions with this switch can result in an inability to start the engine.
Troubleshooting
To troubleshoot, shift the automatic transmission through all gears while trying to start the engine. If the engine starts when in neutral but not in park, this indicates a faulty neutral safety switch preventing starting when the vehicle is not in gear.
To check the switch’s continuity, disconnect the connector and measure resistance values in both neutral and park switch positions. If there is no change detected, it confirms that the switch has malfunctioned.
Solution
Replacing the defective neutral safety switch will enable normal starting operation only when the gear is in park or neutral.
The process of replacing the switch is straightforward for Jeep Compass models, especially when the transmission is already scheduled for fluid service.
6. Security System Defect
One possible reason for experiencing difficulties starting a vehicle is a malfunction in the security system’s immobilizer features.
If the identification codes transmitted by the key fob or chip are incorrect, it can confuse the system and prevent the engine from starting.
Troubleshooting

Consider trying the additional key fob that has been set up for the vehicle – if it enables the vehicle to start normally, the first key fob may be the source of the issue. Also, inspect the dashboard for any security or theft warning lights that are lit up when the starting problem occurs.
You can try to reset the vehicle’s anti-theft module by following a series of specific steps detailed in the owner’s manual. If the lights remain on, it indicates faults in the security system.
Solution
By replacing the faulty key fob that is unable to transmit the correct security code, you can restore the transmission of the accurate identification signals. In some cases, a dealership may be required to reprogram or replace the vehicle’s anti-theft module itself if it malfunctions and leads to starting problems.
7. Blown Fuses or Relays
A blown fuse or a faulty relay within the starting circuit can interrupt the flow of electricity needed to start the engine.
Troubleshooting
The starting system in a Jeep Compass relies on a series of fuses and relays to manage the electrical power to various components, including the starter motor, fuel pump, and ignition system.
If any of these fuses or relays fail, it can prevent the engine from cranking or starting, even though other electrical systems in the vehicle may still function normally.
Solution
To fix a Jeep Compass that won’t start due to blown fuses or faulty relays, begin by identifying the relevant fuses and relays in the starting circuit using the vehicle’s owner’s manual. Inspect each fuse for visible damage and test them with a multimeter for continuity, replacing any that are blown. Similarly, check the relays for damage or corrosion and test them, replacing any faulty ones.
After replacing the defective components, attempt to start the vehicle. If the issue persists, inspect the wiring and connectors for damage, and consider seeking professional help to diagnose and repair any underlying issues causing the fuses or relays to fail.
By addressing issues with blown fuses or faulty relays, you can restore the proper function of the starting system in your Jeep Compass, ensuring reliable engine starts.
Preventive Maintenance: Ensuring Your Engine’s Smooth Operation
While addressing and fixing an existing issue of the engine not starting is crucial, taking proactive measures is essential in preventing future starting problems. Consistently performing preventative maintenance is key in enhancing the dependability and longevity of vital components such as batteries, fuel supply, and ignition.
1. Battery Maintenance
Batteries naturally lose their ability to hold a charge over time due to chemical processes. Regularly checking fluid levels and removing corrosion from terminals can prolong the battery’s lifespan.
It is advisable to conduct load tests on batteries older than 3 years to detect potential failures early on. Replace batteries before they lead to a no-start situation.
2. Fuel System Maintenance
Components like the fuel pump, lines, and filters require regular maintenance to prevent sudden starting issues caused by clogs or malfunctions. Inspect the in-tank fuel pump and replace filters every 60,000 miles.
Utilize fuel injector cleaning additives during oil changes to prevent sediment accumulation. Annually inspect lines and seals for cracks as rubber materials deteriorate after 5-7 years.
3. Optimization of Ignition Performance
As spark plugs accumulate wear and tear over a distance of approximately 30,000 miles, they can diminish both combustion efficiency and the reliability of ignition. Around the 100,000-mile mark, it becomes necessary to replace coil packs and distributor cap/rotor kits due to the deterioration of electrical insulation.
It is recommended to adhere to a maintenance schedule for swapping out worn components and to routinely inspect spark plug gaps during each tune-up. Additionally, it is advisable to clean the magnetic sensor tips within the distributor to prevent fouling problems.
4. Oil Changes
When oil becomes dirty and depleted, it can lead to increased internal mechanical wear and the formation of harmful sludge. It is important to adhere to the recommended oil change intervals provided by the manufacturer, using the appropriate viscosity and quality of oil, such as synthetic blends.
This practice helps to maintain engine efficiency and reduce the likelihood of unnecessary repairs.
Conclusion
Having the knowledge to assess essential systems like fuel, battery, and ignition can aid in identifying starting problems without resorting to guesswork.
With the right troubleshooting skills, you can address issues with a Jeep Compass that is experiencing ‘Jeep Compass Won’t Start but Has Power’ issues.
To summarize, issues with starting when electronics are functioning properly often result from specific problems with battery strength, fuel pump functionality, ignition issues, or occasional mechanical problems in the engine. By methodically testing key components using the prescribed troubleshooting methods, you can pinpoint the underlying cause of the starting problem in your Jeep Compass.
Regular maintenance tasks like fuel injector cleaning can also help prevent future starting issues, providing a long-term solution to avoid recurrent problems.