The Service Electronic Stability Control Jeep (ESC) in a Jeep is a safety feature designed to improve vehicle stability and help prevent skidding or loss of control. Read our guide to find the best quick solutions!
The ESC works by automatically applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power when it detects a potential loss of traction or stability, such as during sharp turns or on slippery surfaces.
How the Electronic Stability Control (ESC) Works?
- Sensors: The system utilizes a range of sensors such as wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors to monitor the vehicle’s movement and identify any deviations from the driver’s intended path.
- Intervention: If the ESC system detects that the vehicle is starting to skid or lose control, it automatically intervenes by:
- Applying brakes: The vehicle can apply brakes to specific wheels individually to assist in steering the vehicle back on track.
- Modifying the engine output: The mechanism is capable of decreasing engine power to decelerate the vehicle and reestablish control.
- Driver Assistance: ESC does not assume control of the vehicle but supports the driver by improving handling, especially in difficult driving situations such as wet, icy, or uneven surfaces.
This system is particularly useful for preventing accidents caused by oversteering, understeering, or sudden maneuvers. It is a standard feature in most modern vehicles, including Jeeps, to enhance safety on the road.

8 Common Electronic Stability Control Jeep Cause and Fixes
1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Cause: The ESC system relies on accurate information provided by the wheel speed sensors to supervise the speed of individual wheels. If these sensors are dirty, impaired, or not functioning properly, they may transmit incorrect data to the ESC module, leading to incorrect functioning of the system.
Fix:
- Inspection: Begin by visually examining the wheel speed sensors positioned near each wheel. Check for any indications of dirt, debris, or physical damage.
- Cleaning: If the sensors are dirty, clean them using a non-abrasive cloth and a gentle cleaner. Be cautious not to damage the sensor during cleaning.
- Replacement: If cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue or if the sensor is physically damaged, it needs to be replaced. Ensure the replacement sensor is compatible with your Jeep model.
- Recalibration: After replacing a sensor, the ESC system may require recalibration, which can be done using a diagnostic tool.
2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
Post-Installation Testing: After replacement, it’s crucial to perform a road test to ensure the ESC system is functioning correctly.
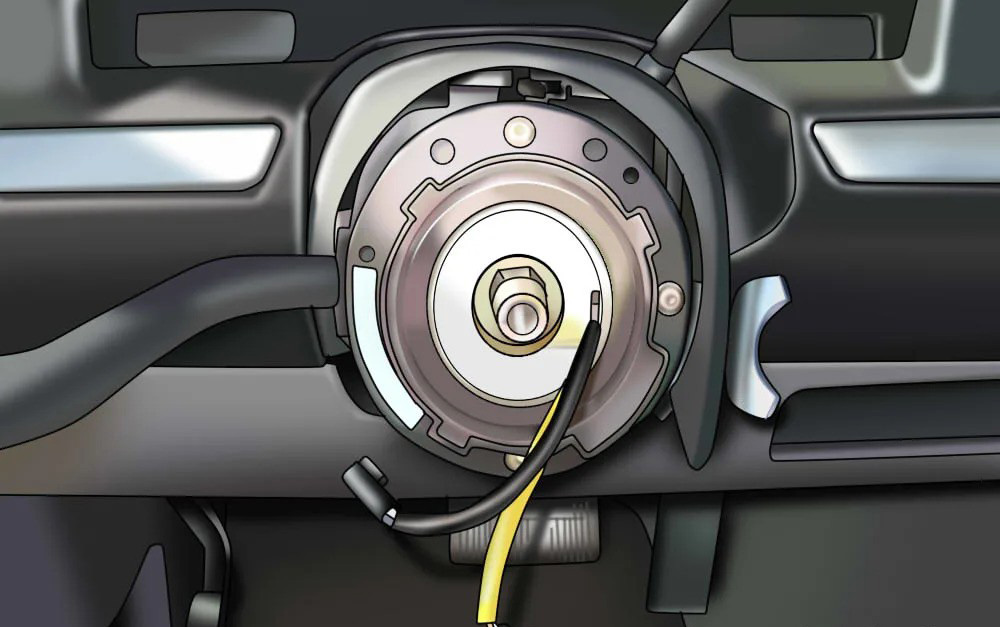
Cause: The steering angle sensor plays a crucial role in providing accurate information about the position of the steering wheel. When not calibrated properly or if malfunctioning, it can cause the ESC system to misinterpret the intended path of the vehicle, resulting in errors.
Fix:
Recalibration: Use a diagnostic tool to recalibrate the steering angle sensor. This process aligns the sensor with the vehicle’s steering system, ensuring accurate readings.
Replacement: If recalibration doesn’t fix the issue, the sensor may be defective and should be replaced. This involves accessing the steering column and installing a new sensor.
3. Low Brake Fluid Level
Cause: The ESC system works in conjunction with the brake system. Low brake fluid can impair braking performance, which in turn affects the ESC’s ability to control the vehicle’s stability.
Fix:
- Check the fluid level: by locating the brake fluid reservoir under the hood and ensuring it is between the “MIN” and “MAX” marks.
- Top Off the Fluid: If the level is low, add the appropriate type of brake fluid (as specified in your vehicle’s manual) until it reaches the recommended level.
- Inspect for Leaks: If the brake fluid level continues to drop after topping it off, inspect the brake lines, calipers, and master cylinder for leaks. Any leaks should be repaired immediately.
- Bleed the Brakes: After adding brake fluid, it might be necessary to bleed the brake system to remove any air that may have entered the lines.
4. Faulty ABS Module
Cause: The ABS module is a crucial component for the ABS and ESC systems. A malfunctioning ABS module can lead to disruptions in the ESC’s functionality, triggering error codes or even a total system breakdown.
Fix:
- Diagnostic Scan: Use an OBD-II scanner to read any error codes related to the ABS system. This can help pinpoint the exact issue with the module.
- Electrical Check: Inspect the electrical connections to the ABS module for corrosion or loose connections. Clean and secure any connections as needed.
- Replacement: If the ABS module is found to be defective, it must be replaced. This involves disconnecting the old module, installing a new one, and programming it to work with your vehicle.
- System Testing: After replacement, perform a thorough test to ensure the ABS and ESC systems are working correctly.
5. Wiring Issues
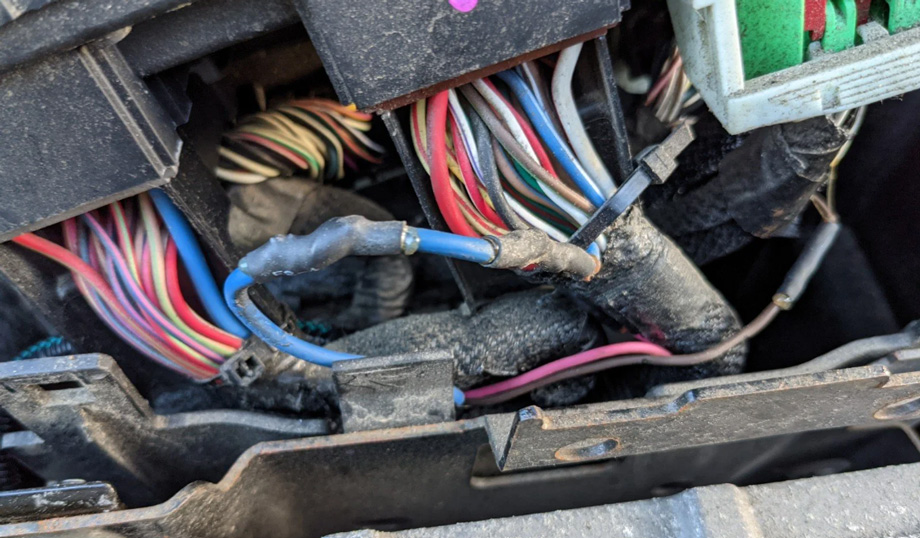

Cause: The ESC system relies on a network of wiring to transmit signals between sensors and the control module. Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt these signals, causing the system to malfunction.
Fix:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the wiring harness associated with the ESC system. Look for any signs of wear, such as fraying, cuts, or corrosion.
- Repair Damaged Wiring: If you find damaged wiring, use electrical tape or heat shrink tubing to repair minor issues. For more severe damage, it may be necessary to replace the affected section of the wiring harness.
- Check Connections: Ensure that all wiring connections are secure and free of corrosion. Clean any corroded terminals and apply dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
- Use a Multimeter: To ensure the integrity of the wiring, use a multimeter to check for continuity and proper voltage throughout the system.
6. Malfunctioning Yaw Rate Sensor

Cause: The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis to assist the ESC system in detecting oversteering or understeering. Malfunctioning sensors can result in inaccurate ESC operation.
Fix:
- Diagnostic Testing: Use a diagnostic tool to test the yaw rate sensor. The tool will check for proper operation and calibration.
- Replacement: If the sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced. The yaw rate sensor is typically located near the center of the vehicle, under the floorboard or within the center console.
- Calibration: After installation, the new sensor must be calibrated using a diagnostic tool to ensure it accurately reads the vehicle’s movements.
- Post-Repair Testing: Perform a road test to confirm the ESC system is functioning correctly with the new sensor.
7. ESC System Software Glitches
Cause: Software glitches within the ESC control module can cause erratic behavior, false error codes, or even complete system failure.
Fix:
- Software Update: Check if there are any available software updates for the ESC system. Manufacturers often release updates to fix bugs and improve system performance. These updates can be installed at a dealership or by using specialized diagnostic tools.
- System Reset: If an update is not available, try resetting the ESC system. This can be done by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for a few minutes, which may clear any temporary software issues.
- Reprogramming: In some cases, the ESC module may need to be reprogrammed to correct software issues. This should be done by a professional with the appropriate tools and software.
- Monitor for Recurrence: After performing these steps, monitor the system for any recurring issues. If the problem persists, further diagnosis may be needed.
8. Damaged Brake Pads or Rotors
Cause: The ESC system relies on the braking system to help control the vehicle’s stability. Worn or damaged brake pads and rotors can reduce braking efficiency, impacting the ESC’s ability to function properly.
Fix:
- Inspection: Visually inspect the brake pads and rotors for signs of wear or damage. Brake pads should have at least a few millimeters of material left, and rotors should be smooth without deep grooves or warping.
- Replacement: If the brake pads are worn down to their minimum thickness or the rotors are damaged, they should be replaced. Use quality replacement parts to ensure optimal performance.
- Brake System Check: After replacing the brake pads and rotors, check the entire brake system, including calipers and brake lines, to ensure there are no other issues.
- Brake Fluid Check: After replacing components, check and top off the brake fluid if necessary, and bleed the brakes to remove any air from the system.
- Road Test: Perform a road test to ensure the braking system and ESC are working properly after the repair.
Addressing these issues typically requires diagnostic tools to pinpoint the exact cause. It’s often recommended to have a professional mechanic handle these repairs, especially when dealing with critical safety systems like ESC.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Electronic Stability Control Jeep (ESC) system is a vital safety feature in modern vehicles, including Jeeps, designed to help maintain control and prevent skidding in challenging driving conditions. However, the system can be compromised by a variety of issues, ranging from faulty sensors and low brake fluid to software glitches and wiring problems. You can view the latest forum discussion Here for further info.
Identifying the root cause of ESC malfunctions is crucial for ensuring the system functions properly, and addressing these issues promptly can significantly enhance driving safety. Whether it’s recalibrating sensors, updating software, or replacing worn components, maintaining the ESC system in optimal condition is essential for a safe driving experience.